As I start to make some progress on my new research project on travel, health and risk I am turning my attention to the sorts of things that early modern travellers were fearful of. As a bit of a nervous traveller myself, it’s quite comforting to know that there is actually a long history of travel-related anxiety.
From the early modern period, domestic and international travel were beginning to increase due to many factors including commercial expansion and the Atlantic economy, religion and mission work, military and diplomacy, as well as technological developments and the growth of travel infrastructure. For the first time in history, large numbers of travellers were beginning to explore both their own countries and wider world, encountering new countries, environments, and peoples.
Unlike today, when it’s entirely possible to have breakfast in London, lunch in Milan and be back at home in time for supper, travel in the early modern period was no easy undertaking. More than this, it was widely acknowledged to be inherently dangerous. What, then, were the perceived risks? Even a brief survey tells us a lot about how travel was regarded in health terms.

First was the risk of accident or death on the journey. In the seventeenth century even relatively short distances on horseback or in a carriage carried dangers. Falls from horses were common, causing injury or even death. As Roy Porter noted, when the wife of Justinian Paget was thrown from her horse in October 1638, it was said to be the ‘cause of all her future sickness’. In Monmouthshire in 1657, one Francis Bradford was killed as his horse bolted, throwing him over its neck with his feet caught in the stirrups. ‘His wyfe was with hym and she presentlie alighted from her horse and cryed for helpe’. Many drownings occurred as people tried to cross rivers on horseback and fell in or were swept away.
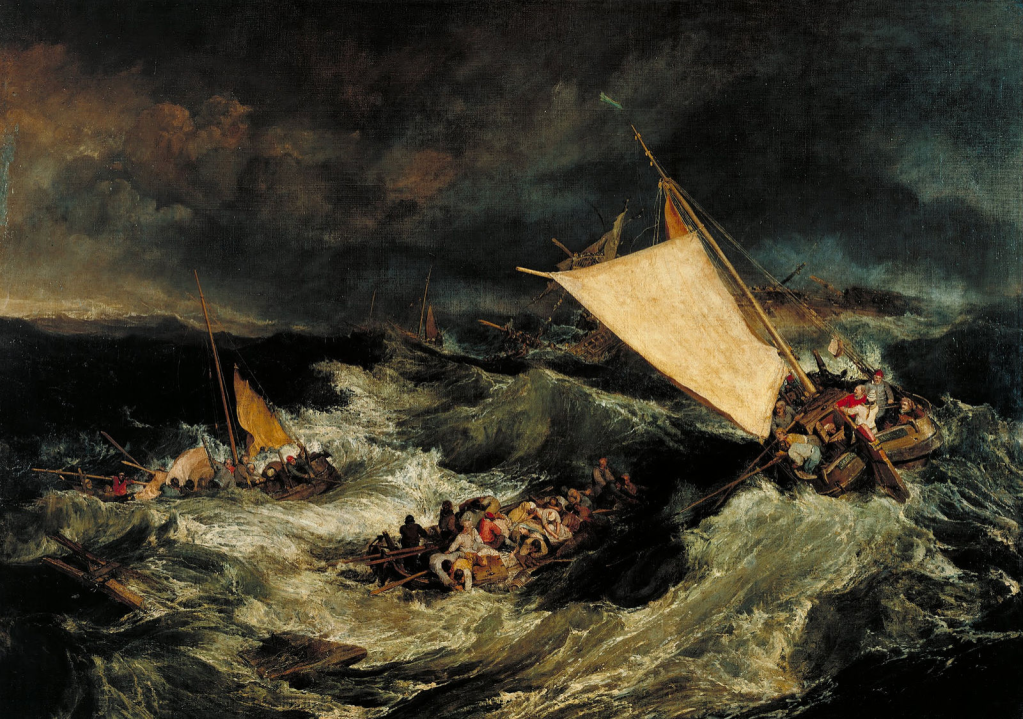

Travel by sea, even around local coasts, carried its own obvious risks of storm and wreck. So common and widely acknowledged were the vagaries of sea travel that a common reason for making a will in the early modern period was just before embarking on a voyage. The language used in these formulations is telling. In 1638, Edward Harthorpe, Richard Veesey, Michael March and Thomas Huckleton, ‘with divers others’, made their will, ‘being bound to take a voyage to Canady (sic) in America, w(hi)ch being a daingerous voyage, and they putting theire lives to hazard therein, did consider their mortalitie’.
This was a common theme, and the prospect of the impending journey, and the not-unreasonable assumption that they might not return, led many to consider putting their affairs in order. This anxiety was neatly articulated by Thomas Youngs in 1663, ‘Being bound upon a voyage to sea, and calling to remembrance the uncertain state of this transitory life, and that all fleshe must yielde undo death…’. One intent on the journey, travellers wanted to be prepared in body and soul.

Once abroad, too travellers were at the mercy of a bevy of dangers, from unfamiliar territories and extreme landscapes to harsh weather and climate, their safety contingent on the quality of their transport and the reliability of their guides. In 1793 Useful Instructions for Travellers contained chapters advising travellers as to how to deal with the many and various dangers to life and health that they might face. These included the necessity to frequently open carriage windows to refresh the air, the need to take a small medicine chest to attend to wounds (including falls from horseback), and various preparations to treat the haemorrhoids that often accompanied long periods in a sitting position.
Knowledge of the conditions, climates and environments of intended destinations was also key. Ideally, a traveller should be able to ‘cure himself of some distempers’, be wary of the change of air and the hazards of the journey, and to take their own store of medicines in case they were hard to procure once abroad.
But some even considered the whole process of travel itself to be potentially harmful to the body. Even in the sixteenth century, ‘The Hospitall for the Diseased, wherein are to bee founde moste excellent and approued medicines’ included a list of things considered bad for the heart. As well as what the author viewed as deadly vegetables such as beans, peas and leeks, further heart problems might be caused by ‘too much travell’, or even ‘drink[ing] cold water after travell’. Similarly, in a section about things that are ‘ill for the brain, A.T.’s 1596 A.T., A rich store-house or treasury for the diseased noted “Overmuch heate in Trauaylinge”.

Scurvy was another condition firmly linked to travel. In 1609, Petrus Pomarius’, Enchiridion medicum viewed scurvy as an occupational hazard for ‘those that trauell by sea, by long voyages; and our fishers that travel to the Newfound-lands’. As well as the perils of the long journey, the problems could arise due to the ‘stincking waters, & especially in an hot aire’ that travellers were exposed to. Climate – and particularly heat – was considered risky. In the 1793 Etmullerus abridg’d: or, a compleat system of the theory and practice of physic, Michael Etmuller stated that travelling in a hot climate could cause wakefulness and perturbation of the mind.
Even ‘foreign’ food and drink could be risky. Thomas Tryon’s Miscellania (1696) noted the dangers of ‘intemperance’ and of misjudging the effects of climate upon the body in regard to drinking alchohol. According to Tryon, many English travellers were ‘much Distemper’d, and many die when they Travel into the West and East Indies, because they take wrong measures, continuing the same disorder and intemperance as they did in their own Country’.
Travel, then, was a risky business, and one that individuals would not have undertaken lightly. There were a range of factors to consider, from basic risks of life and death to the dangers of particular conditions and climates, food and illness.